Football is nowadays one of the most popular sports in our country and one of the most economically active. Its practice requires the athlete to make the most of his or her conditional qualities, such as basic movement patterns, strength, flexibility, speed and power, which means that the athlete must assume a great sporting commitment. The level of competitiveness is higher every day due to the demands of the game and the competition.

For this, there must be several people capable of optimising this performance. Among these professionals we find the figure of the physiotherapist.

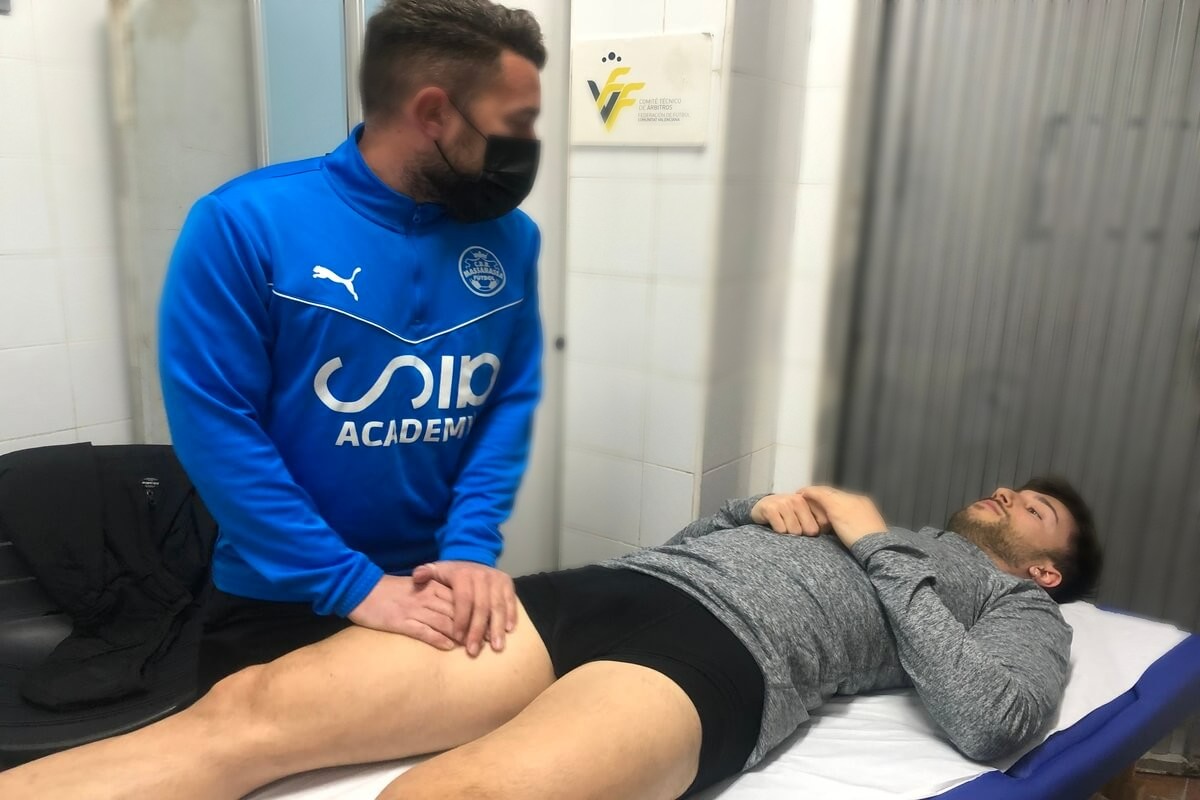
The role of the physiotherapist in football
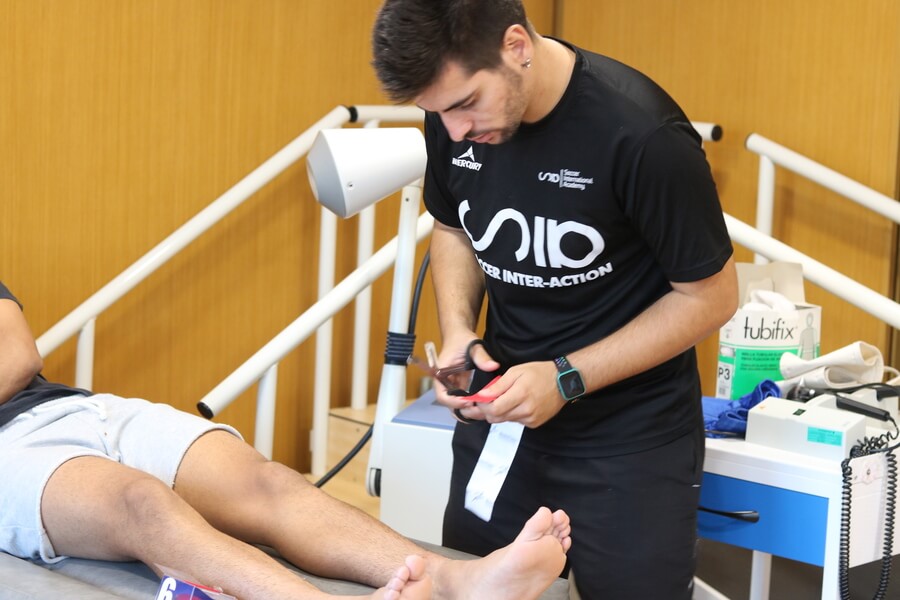
His work consists of planning and executing therapeutic strategies so that the athlete can optimise both the results and the time spent. The task of recovering the functionality of the athlete as soon as possible will always be complex, as the processes have their own physiological process of recovery and repair, but it will be essential or of great importance to be able to count on this professional.
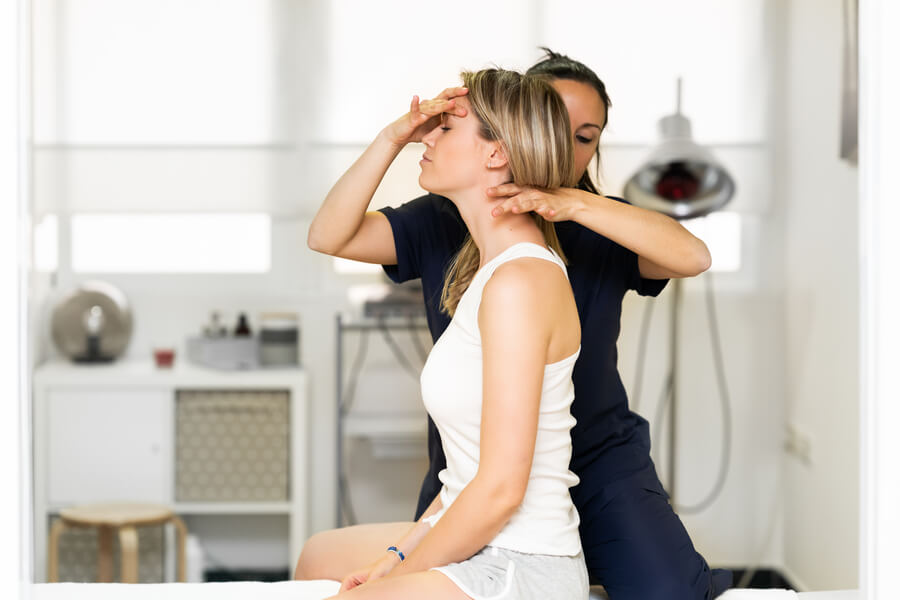

Role of the physiotherapist in football
In the practice of this sport we often find football players who have been out of the game for several months, sometimes without knowing how to measure the time of the injury process or the loads for their gradual return to the field of play. Their work is carried out both on and off the pitch in order to be in optimum condition to meet the athlete’s performance requirements.
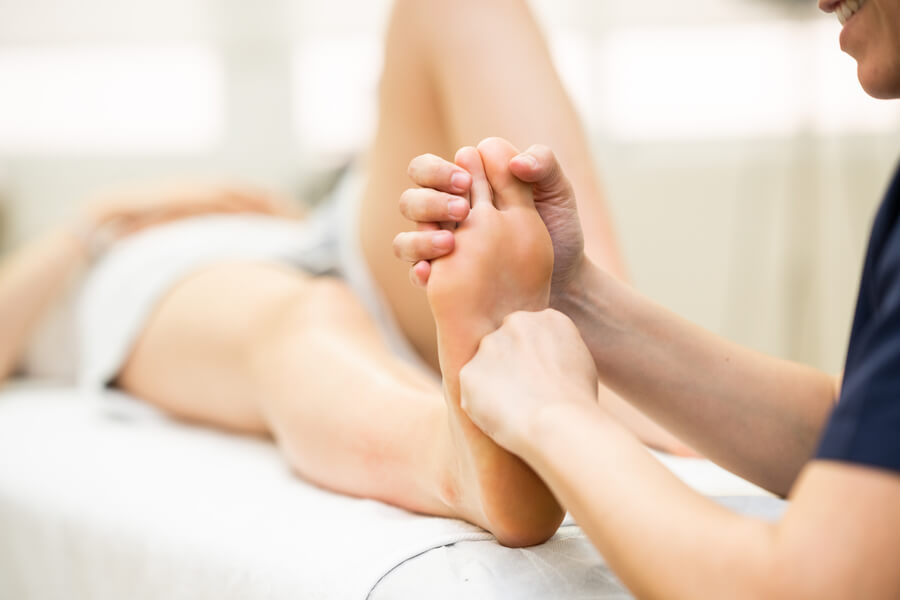

The athlete, generally, wants a short recovery process, without thinking that the adaptive process of the damaged structures for a guaranteed return is of vital importance. There is a large percentage of footballers who, if they do not maintain the recovery process within the established time, relapse in their injury.
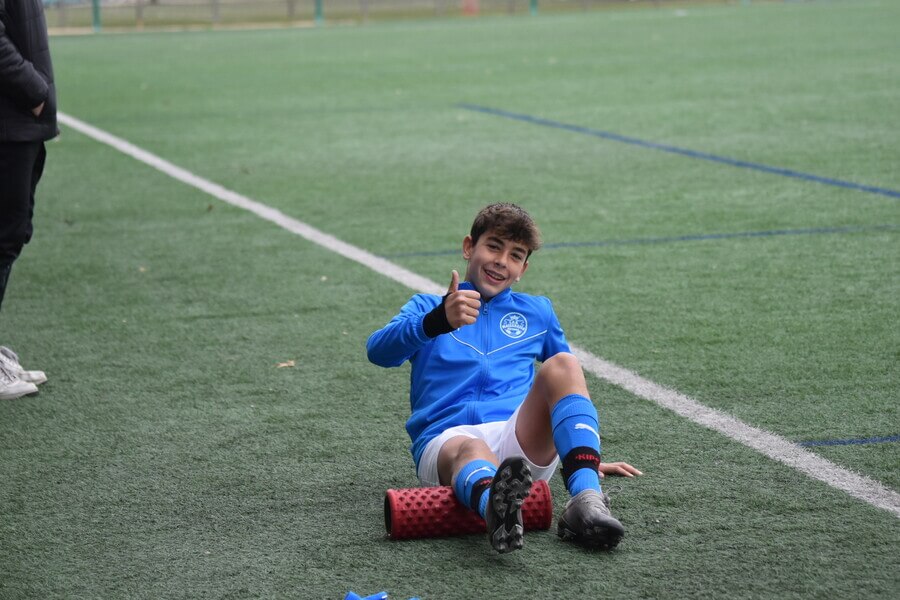

What is the role of the physiotherapist in football?
- Dissemination: Ethical duty to advise the athlete in carrying out actions that contribute to improving prevention conditions.
- Planning: Participate in the planning from the pre-season of the teams together with the staff area, coaching staff and the rest of the team’s professionals.
- Prevention: Avoiding those factors that could cause injuries caused by sporting activity, associated injuries and/or sequelae of the primary injury, and their possible recurrence.
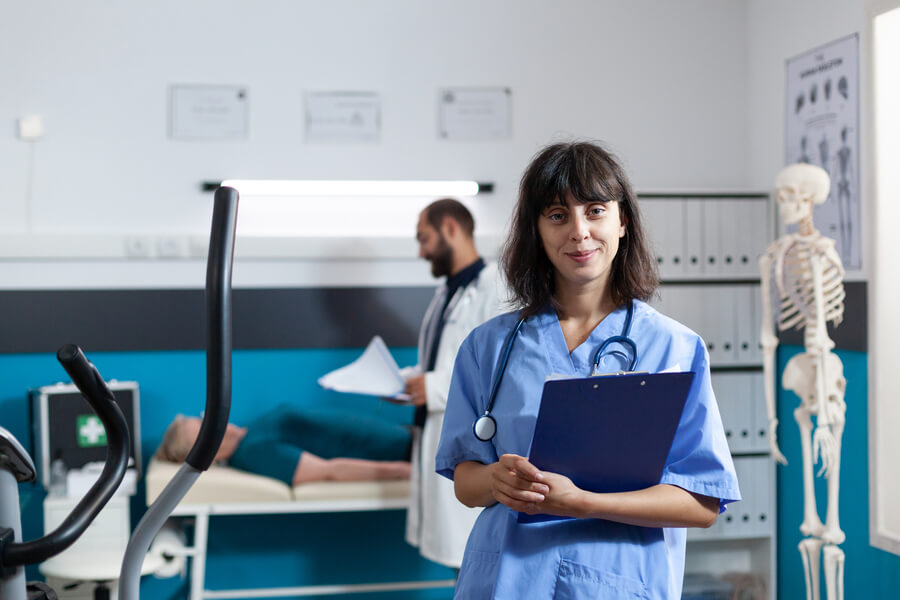

- Recovery: The sports physiotherapist will apply the treatment considered for the injury and associated injuries, trying to alleviate the pain and keep the player away from the field of play for the shortest possible time.
- Readaptation: The process that must take place in order for the athlete to start practising sport in the appropriate conditions, similar to the one he/she had before the injury. These strategies of physical preparation physiotherapy techniques can range from stretcher work to prevention and strength sessions.
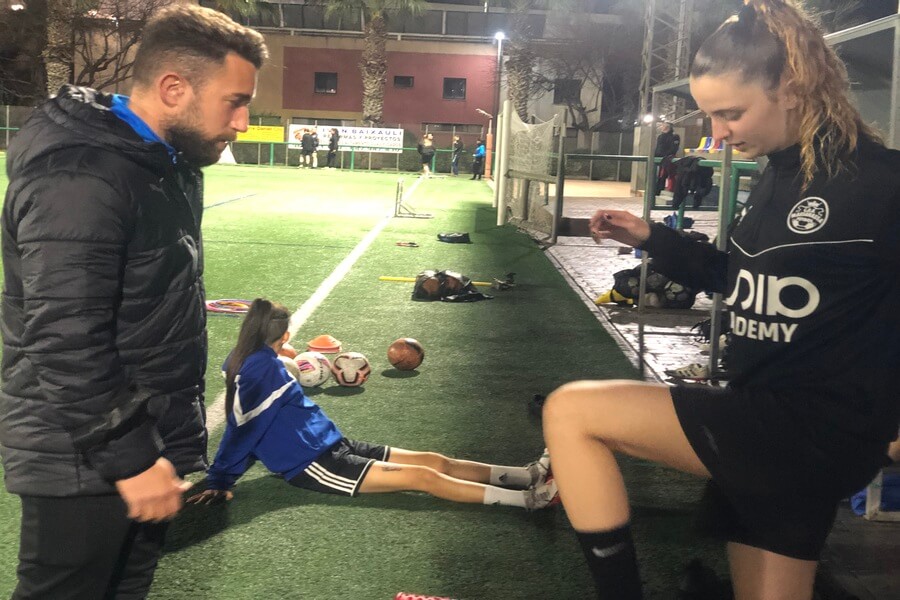

What are the most common injuries in football?
When talking about the most frequent injuries in football, we must refer to muscle injuries before others such as fibrillar ruptures.
Firstly, it is a sport that requires explosive efforts and repeated changes of rhythm, which generate great demands of intensity to the musculature, or there are moments of a large number of accumulated matches, whether we are talking about grassroots football or the components of the Spanish national team, based on this… it is necessary to have professionals such as the physiotherapist, who together with other professionals such as retrainers or physical trainers can help the athlete to maintain the necessary conditional demands.

The muscle is stressed and excessive sweating occurs. This generates a loss of minerals such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, in addition to the loss of water, so the body suffers dehydration processes. If we do not rehydrate sufficiently or follow a good diet, the muscle suffers and can be a cause of possible injuries.

Other factors influencing injuries
- The temperature in the environment when playing. If it gets colder there is less blood supply to the muscle or blood circulation, which, when a contraction occurs, there is an increased risk of injury.
- Nutrition. We can help prevent muscle injuries (the most common injury in this sport) by having optimal levels of collagen. We have foods that provide us with collagen naturally and that are rich in protein and vitamins C, E, B1, B2, B6, coenzyme Q10 and magnesium. The excess of acidifying foods can produce acidosis in the tissues, that is to say, toxins accumulate that make the tissues more rigid and, therefore, there is a greater risk of suffering fibrillar breaks and tendon degeneration.
- The surface. In this case, it is the tendons that suffer the most, as they are the ones that adapt to the hardness of the terrain. Training should be carried out on suitable surfaces.