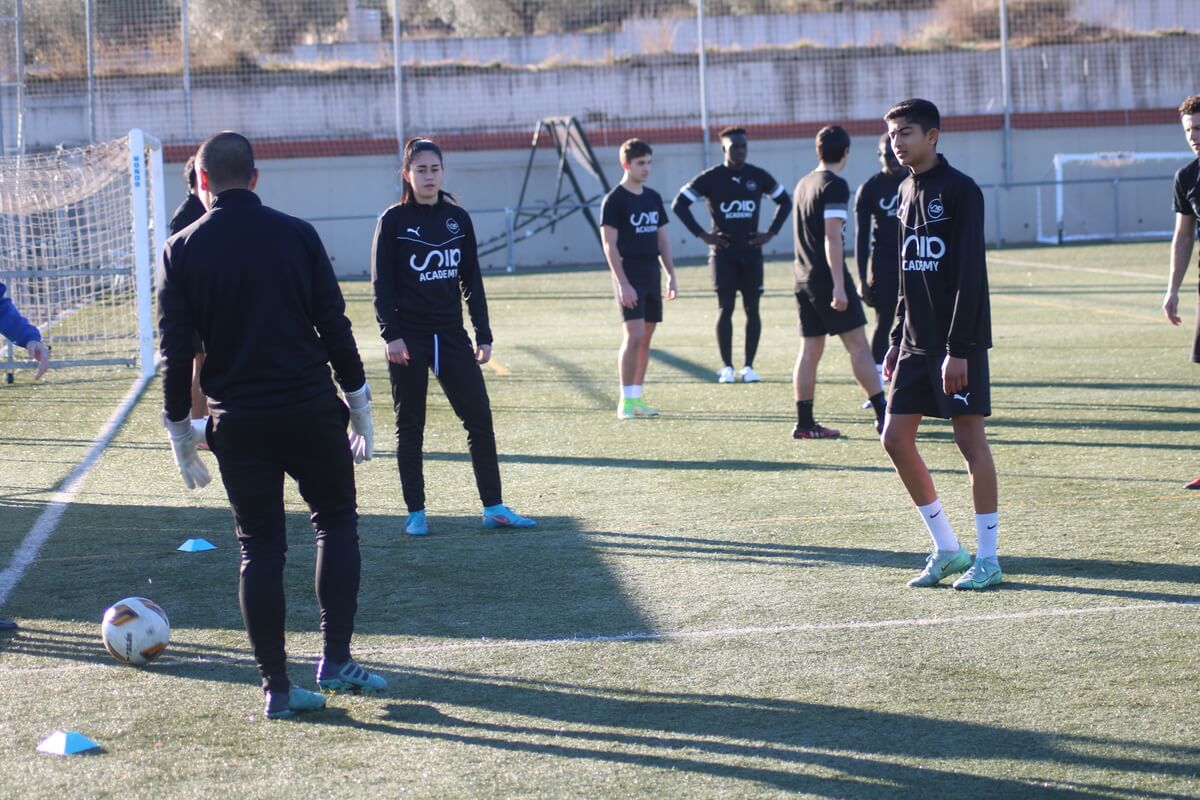
How is psychology applied in football?
The knowledge about psychology is very broad, but where these aspects really become important is in how we solve our difficulties or improve our skills in practice. In order to achieve this increase in performance, knowledge must be applied in a context very close to the real one, generating situations close to the action where we want this learning to take place.

This learning can take place in two environments: individual learning, outside the playing field by generating different techniques and guidelines to solve certain situations; or through collective actions during the tasks that can be carried out in training sessions.

Individual learning in football
Through individual intervention we can improve the athlete’s skills to improve their self-awareness and learn to control themselves in different situations, as well as teaching them to improve their levels of activation, thought control, attention and management of stressful situations. To achieve the improvement of the aforementioned skills it is very important to establish an individualised plan for each player.

To start this individualised plan, the player must first be evaluated by means of semi-structured interviews and player tests, to get to know his or her sporting and family environment and to carry out video analysis of his or her actions. Based on this objective and subjective information, we will have to create an action plan with the psychological competencies that each player must improve, with a retest to re-evaluate the knowledge learned.

Benefits of individual learning
In this competition plan it is important to provide the players with practical strategies and techniques that they can develop while they carry out the sporting activity, having more capacity to solve problems than their teammates and rivals. These strategies should be improved with practice and effort, making them automatic until they are performed unconsciously, as happens unconsciously in the rituals we perform before taking a free kick or corner kick.

This process is not watertight and permanent, but it is important to continually reinforce the skills acquired in order to maintain them and continue improving. If they do not continue to improve, it is possible that these strategies may be forgotten or have less effect, which is why it is important that seeing a psychologist is continuous and not just a tool to be used when there are difficulties.

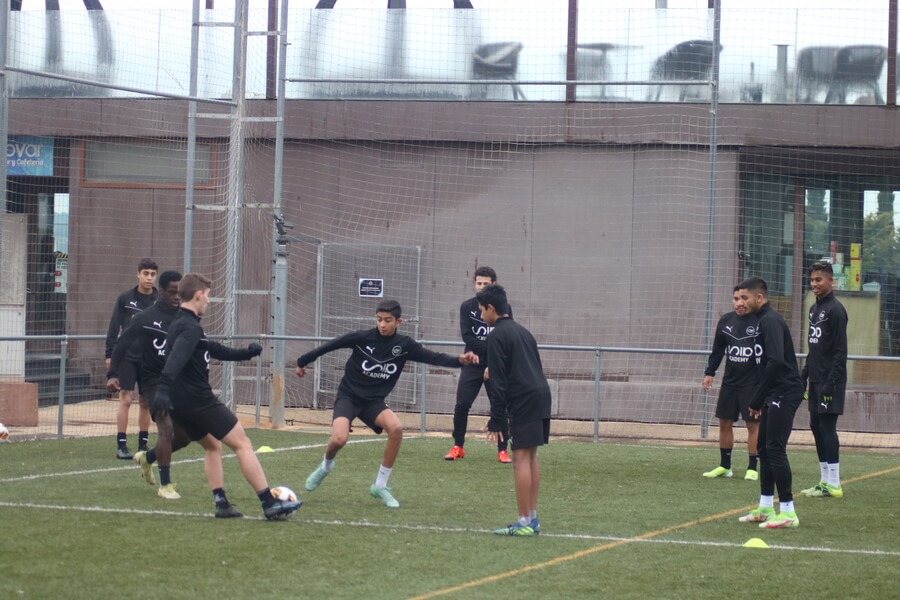
Team learning in football
They serve to generate a level of cohesion and maximum performance with the approach of competitive strategies. An example of the importance of psychology in the tasks is as simple as in a 5×2 rondo and the amount of mental processes that are performed: attention to the ball and vigilance in addition to teammates, the speed of processing and action planning, activation control…
All these components are present in all tasks and it is important to identify them and to identify the cognitive load of the tasks and the cognitive demand can increase the fatigue of the players causing a worsening of their performance.

How to carry out these strategies during training
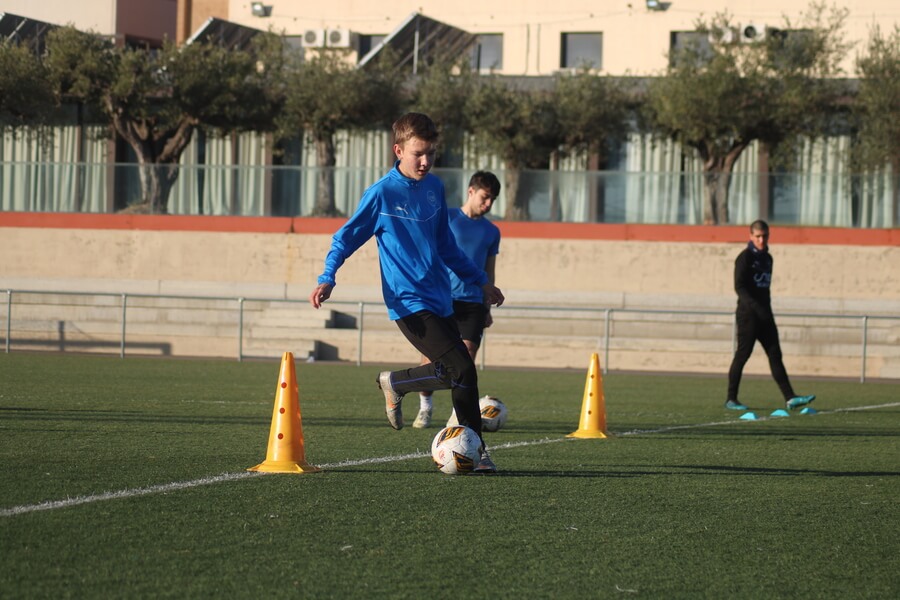
To encourage competition under high pressure, it is important to reproduce in a controlled way during training different situations to generate stress, in order to encourage playing under high sporting pressure and to be able to better control stress management in matches during competitions.

Being aware that it is very difficult to resemble the conditions of competition (this being one of the most important attractions of competition), we must, in the tasks, aggravate the stressful conditions in order to habituate the organism and reproduce as closely as possible what it will encounter in a competitive context.

Factors modifying the training context
The factors that we can modify to increase the stress of the players are time, dimensions, technical rules, tactics, conditioning, rewards or punishments and the result.

Applying these concepts can help the individual to improve the management of their emotions and anxiety control, as well as improve their cognition and performance on the field. For coaching staffs, they should give the psychological burden of the tasks the value it has by giving a different tool to their players and teams to improve.