NUTRITIONAL STRATEGIES DURING COMPETITION
Los objetivos nutricionales durante esta etapa se enumeran a continuación:
Carbohydrate intake in its simplest form
El aporte de carbohidratos durante una competición tiene la finalidad de suministrar energía rápida al torrente sanguíneo a fin de disminuir la velocidad de consumo de las reservas (glucógeno), favoreciendo así su duración y previniendo la aparición de fatiga.
La evidencia científica en fútbol muestra beneficios en el rendimiento tras el consumo de carbohidratos durante la competición tales como: mejora de la velocidad de regate y pases, mantenimiento de carreras de alta intensidad, entre o otros.

The recommended intake during a match is 30 to 60g of carbohydrates just after warm-up and at half-time. It is recommended to cover this intake from gels or sports drinks which tend to improve tolerance and prevent gastrointestinal problems.
Factors determining the efficiency of carbohydrate use during competition
- Time: this is the main determinant, as for interventions lasting less than 30 minutes, no additional input is required.
When the intervention is longer if there is a proven benefit:
- From 45 min to 75min: isotonic drinks could be enough.
- From 1h to 2h: 30g/hour is recommended, if the time is longer we can increase to 60g/hour. The recommended intake time is just after the end of the warm-up and at half-time.
It is recommended to cover this intake with gels or sports drinks, which tend to improve tolerance and prevent gastrointestinal problems.

Fluid replenishment to maintain adequate hydration status
The amount of fluid to drink during competition will depend on the sweat rate of each player, which in turn will be determined by the intensity of the exercise, environmental conditions, acclimatisation capacity, genetics and other factors.
Sweating rates estimated from studies in football players range from 0.5 to 2.5 litres/hour.

POST-COMPETITION NUTRITIONAL STRATEGIES
During this phase the aim is to reduce the time needed to fully recover. Within the recovery strategies, nutrition has a profound influence on the process as adequate nutrient availability will allow not only the prompt replenishment of energy but also the correct adaptation of the muscle to the training stimulus.
Energy replenishment is especially important when there are multiple matches in a week and recovery from one match becomes preparation for the next. In these cases, faster recovery would be an important advantage.
On the other hand, many of the adaptations we are interested in to promote performance in football occur within the muscle. New research supports that you can accelerate the organismic response to protein synthesis after exercise by optimising the quantity, timing and quality of protein intake after training and matches.
The nutritional objectives during this stage are listed below:
Replenish energy reserves
Post-match meals or snacks should target a carbohydrate intake of approximately 1g/kg/hour for 4 hours.
The intermittent nature of exercise during matches is associated with rapid breakdown of muscle and liver glycogen. It has been shown that muscle glycogen stores are often depleted at the end of a match and this has been correlated with a decrease in total distance covered and a reduced ability to sprint.
Carbohydrate replenishment is therefore the main objective of recovery as it guarantees an efficient return to normal physiological function, a decrease in muscle soreness and the disappearance of psychological symptoms associated with extreme fatigue.
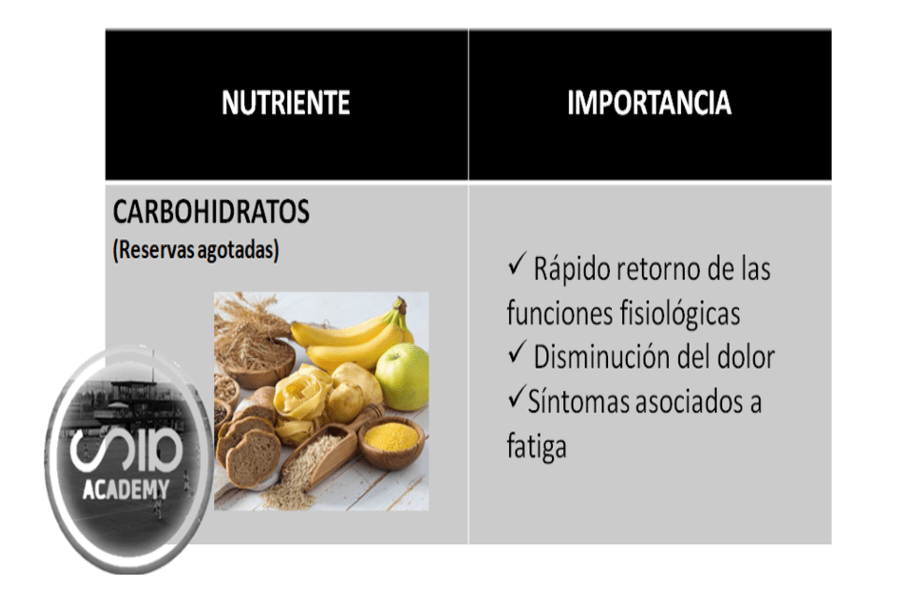
Optimising protein synthesis
Consuming protein immediately after training provides a source of amino acids that promote muscle growth and repair more efficiently by activating protein synthesis.
It is for this reason that a protein intake of 0.3 g/kg body weight (20-25g) is recommended, which has been shown to promote muscle adaptation and the repair of muscle cells damaged by the impact that frequently occurs during football matches.
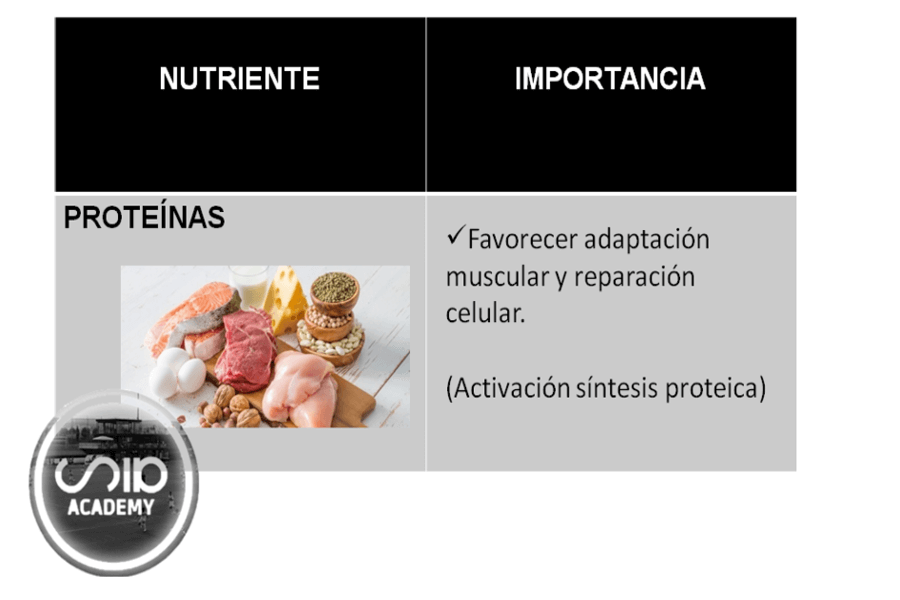
Combination of for recovery
Studies have shown that co-ingestion of carbohydrate and protein is more effective in stimulating anabolism compared to carbohydrate-only ingestion after exhaustive aerobic exercise..
As described above, the combination of carbohydrate and protein immediately after exercise (first 2 hours) is an easy strategy for players of all levels.
Sports drinks and foods often have ideal amounts of nutrients for recovery, these can be an option for players who find it difficult to plan post-match snacks in advance.

For more examples and further information see the BLOG on nutritional strategies to support recovery.






