A footballer who faints on the field can be an alarming situation. A prompt and appropriate response is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of the affected player. This article provides guidance on how to respond to such incidents. It will cover the steps to take, from the initial assessment of the player to the importance of seeking medical help and what to avoid in such cases.
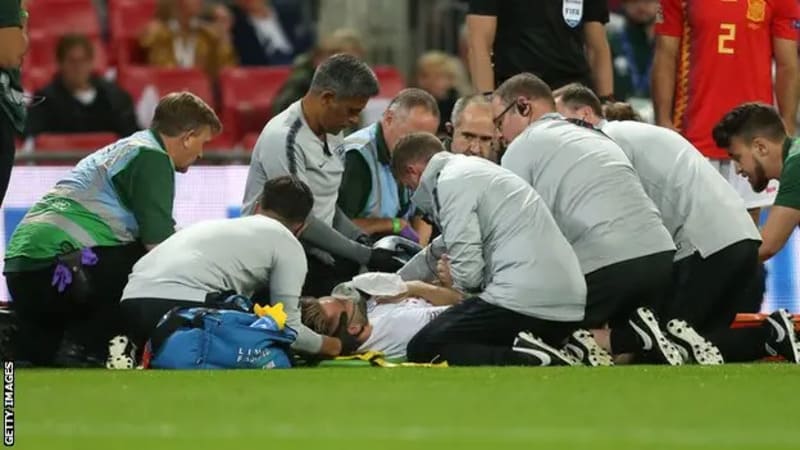

Table of contents
Initial player evaluation
The initial assessment of a fainted football player is a crucial step in determining the severity of the situation and taking appropriate action.
Check if the player responds
The first step is to check the player’s response. It is essential to approach the player calmly and not move him if he does not respond, to avoid possible cervical injuries. You can try to gently shake him by the shoulders while asking him if he is okay.
Identify possible causes of fainting
Possible reasons behind fainting need to be considered as this may influence subsequent care.
Dehydration and exhaustion
One of the most common factors in fainting during sports is dehydration. When a player does not receive enough fluids, he or she may experience extreme fatigue leading to loss of consciousness. This risk increases if he or she has been running intensely without adequate fluid intake.
Bumps and traumas
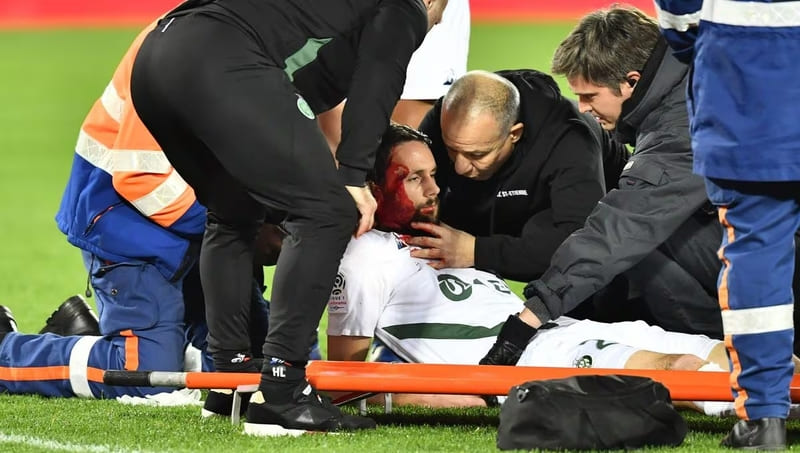
Impacts during play, such as blows to the head or falls, can also cause fainting. A contusion or a concussion are situations that should be considered seriously, always looking for signs of injuries that may have contributed to the loss of consciousness.
Pre-existing medical conditions
Certain existing medical conditions, such as heart or neurological problems, may predispose players to fainting. It is important to know the player’s medical history in order to provide appropriate and effective care.
Check if the player is breathing
It is essential to check the player’s breathing after a fainting spell. This assessment will help determine the next course of action and ensure that the player receives appropriate care as soon as possible.
Forehead-chin maneuver
The chin-lift maneuver is a technique that allows the airway to be opened, making it easier to check the player’s breathing. This procedure is key to ensuring that there are no obstructions preventing air from entering.
How to open the airway
- Place one hand on the player’s forehead to gently press backward.
- Using your other hand, lift the player’s jaw up and forward.
- Ensure that the tongue does not obstruct the airway when maintaining this position.
Check breathing
Once the airway is open, it is critical to observe and listen to the player for breathing. For a few seconds, the following guidelines should be followed:
- Observe the movement of the chest to detect if there is elevation.
- Listen to breathing sounds near the mouth.
- Feel the breath on your cheek.
Mandibular thrust maneuver
In some cases, it may be necessary to use the jaw thrust maneuver to open the airway, especially if a cervical spine injury is suspected.
When to use it
This maneuver is recommended when there are signs of cervical injury, as it prevents movement of the neck and head during the opening of the airway. It is used when the head tilt-chin lift cannot be performed safely.

Correct procedure
- Place your index fingers on the bottom of the player’s jaw.
- Lift the jaw up, keeping the head in a neutral position to prevent any further damage.
- Check for signs of breathing in this position.
Seek medical help
It is crucial to act quickly when calling for medical help when a footballer faints. The information provided to emergency services can be crucial to the proper care of the affected player.
Local emergency number
It is essential to be informed about the emergency number at the location of the sporting event. In many countries, the main number is 112. Keeping this information accessible and always at hand can save vital time.
Information needed for medical services
When contacting medical services, it is essential to provide clear and accurate information. This will allow medical staff to be prepared to deal with the situation appropriately.
Player status
- Indicate whether the player is conscious or unconscious.
- Check for breathing and mention any breathing difficulties.
- Report any possible injuries that may have caused the fainting.
Incident details
- Describe the circumstances in which the fainting occurred, such as whether there was a blow or whether any unusual behavior was observed before the fall.
- Provide information on the duration of the faint and the player’s reactions.
- Share relevant data about pre-existing medical conditions that the footballer may have.
Act based on whether the player is breathing
Knowing how to react based on the player’s respiratory status is crucial. The actions to take vary depending on whether the player is breathing or not, and each situation requires immediate and appropriate attention.

The player breathes
Lateral safety position
If the player is determined to be breathing, he or she should be carefully placed in the lateral recovery position. This position helps keep the airway open and reduces the risk of aspiration should the player vomit or produce excessive saliva.
Cervical control during turning
It is essential that the turn to the lateral position is done with cervical control, especially if there is suspicion of neck injuries. This procedure should be carried out by at least two people:
- A person should ensure that the head and neck are aligned with the rest of the body during the movement.
- The other person can help turn the player gently, taking care not to force sudden movements that could aggravate an injury.
The player is not breathing
Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
In the event that it is confirmed that the player is not breathing, it is vital to begin CPR immediately. This action can be crucial to saving his life, as it restores blood circulation and oxygenation of the organs.
Chest compression frequency and depth
Chest compressions should be performed at a rate of 100 compressions per minute. The appropriate depth is approximately 5 cm, which will ensure that sufficient pressure is generated in the heart to pump blood effectively. It is important to maintain the pace and not stop until medical help arrives or the player shows signs of recovery.
What to avoid doing in case of fainting
In critical blackout situations, it is essential to know not only the appropriate actions, but also the most common mistakes to avoid. These wrong actions can complicate the situation and cause additional damage to the player.
Do not put your fingers in your mouth
Putting fingers in a player’s mouth is a myth that can cause more problems than it solves. This action is not necessary and can introduce dangerous risks.
Risks of putting your hand in it
- Airway obstruction, making the situation worse.
- Additional injuries to the jaw or teeth.
- Possibility of triggering a gag reflex, increasing the risk of choking.
Do not move the player without cervical control
It is essential not to move the player without proper control of his neck and head. Sudden movements can cause severe damage, especially if there is suspicion of a spinal injury.
Do not allow the player to get up quickly
Lifting the player too quickly can cause his condition to worsen. The cardiovascular system may not be able to withstand a sudden change of position, which could cause him to faint again.
Do not feed or drink
Offering food or drink to a player is a dangerous practice. Ingestion can cause choking, especially if the player is not fully conscious and alert.
Avoid applying cold water or getting the player wet.
Using cold water on the face or dousing the player is considered counterproductive. This can cause additional shock and interfere with medical care that may be needed later.
Importance of first aid training
First aid training is essential in the sports field. Correct training can make all the difference in critical situations and contribute to the safety of players on the field.
First aid courses for players and coaches
Taking first aid courses is a recommended practice for all team members. These courses provide theoretical and practical knowledge that is vital in emergencies. Some of the topics covered include:
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques.
- Management of common injuries in football.
- Identifying signs of dehydration and exhaustion.
- Protocol for action in the event of fainting or other emergencies.
Training should be ongoing, regularly updated to include new techniques and protocols. Integrating this training into the training routine reinforces the ability to respond quickly to incidents.
Collaboration with emergency organizations
Collaboration between football academies and emergency organisations, such as the Red Cross, can enrich first aid training. These partnerships offer the resources, materials and expertise needed for effective teaching. The benefits of collaboration include:
- Access to qualified trainers with extensive experience in emergencies.
- Training on the use of medical equipment and defibrillators.
- Simulations and practices in real or controlled situations, improving participants’ confidence.
Fostering these types of collaborations also helps to create a support network in case of emergencies, ensuring that both players and coaches are prepared to act. Safety in sport begins with proper preparation and education.
Relevant cases and lessons learned
Analysis of incidents in football provides important insights into the management of on-field fainting. Through a variety of cases, valuable lessons can be drawn that contribute to improving safety in the sport.
The case of Fernando Torres
One of the most shocking episodes in the recent history of Spanish football occurred during a match where Fernando Torres fainted after a collision. This incident caused great concern both among the public and the team’s medical staff.
The situation was handled effectively thanks to the quick intervention of the medical staff, who applied the appropriate techniques to ensure the player’s health. Torres was quickly transferred to a medical center, where he received specialized care. This case highlighted the importance of:
- Training medical personnel in the recognition and treatment of fainting.
- The need to maintain standardized emergency protocols at all levels of sport.
- Ongoing training of support teams in first aid.
Other incidents in football
Over the years, there have been multiple incidents of fainting in football, each providing valuable lessons. These cases can range from severe dehydration on hot days to adverse reactions to pre-existing medical conditions.
Some of the featured events include:
- The fainting of some players during international tournaments due to pressure and extreme exhaustion.
- The fall of a player in a local championship after an impact that caused a temporary loss of consciousness.
- Situations in which a lack of hydration and adequate rest has led several footballers to collapse on the pitch.
These incidents underline the importance of:
- Provide adequate supervision of players’ health during training and matches.
- Implement training on fainting identification and management in clubs.
- Raise awareness of the importance of hydration and physical health among all players.
Preparation and prevention in the academy
Preparation and prevention are essential in the environment of a football academy. Having clear protocols and adequate equipment allows for an effective response to risky situations, thus ensuring the safety of footballers during training and matches.
Emergency protocols for training and matches
Establishing emergency protocols is essential to ensure that all team members are prepared to act quickly and appropriately in the event of a critical situation. These protocols should be known by everyone, including players, coaches and support staff.
- Conduct periodic drills to practice implementing protocols.
- Make sure each person knows their role in an emergency.
- Clearly define the steps to follow in the event of a player fainting, including communication with emergency services.
Essential equipment on the playing field
Proper equipment is vital for emergency management. Having the right materials and tools can make all the difference in critical situations.
- First Aid Kit: Should be well stocked with bandages, dressings, scissors and other basic medical supplies.
- Automated External Defibrillator (AED): A device that can be key to resuscitating a player who suffers cardiac arrest.
- Hydration equipment: avoiding dehydration is crucial; make sure there is enough water and isotonic drinks available during training and matches.
- Means of communication: have mobile devices or radios to quickly coordinate actions in case of an emergency.






